Applications of Compression Molding,Compression molding is a manufacturing process that has stood the test of time, proving its worth across various industries. It involves shaping materials under heat and pressure, utilizing a compression mold to create parts with precise dimensions and complex geometries. This process is particularly renowned for its ability to work with composite materials, which has led to its widespread use in producing components that require a high strength-to-weight ratio
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Compression Molding
At its core, compression molding is a straightforward yet effective technique. The process begins with the placement of a pre-measured amount of material, known as a “charge,” into a heated mold cavity. The compression mold, typically made of aluminum or steel, is then closed using a press, which applies the necessary pressure to shape the material. Heat and pressure are maintained until the material cures or solidifies, after which the finished product is removed. This method is not only efficient but also allows for the production of parts with intricate details and features such as threads, holes, and grooves.
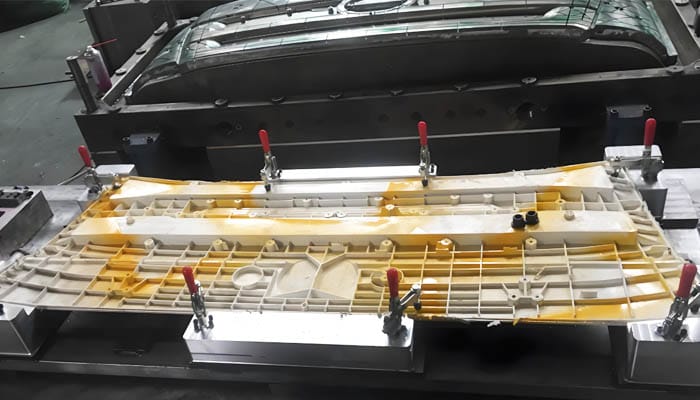
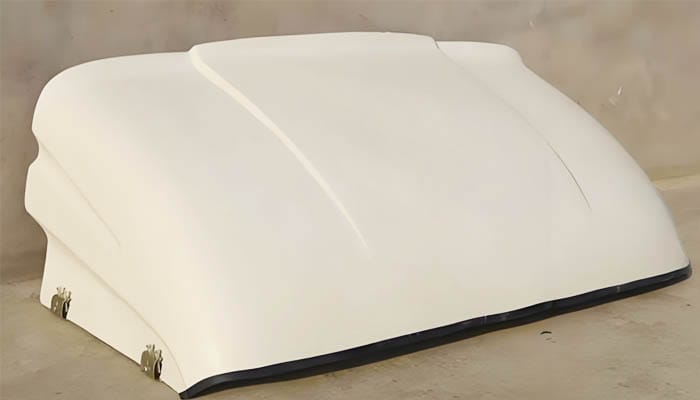


The Role of Composite Materials
Composite materials play a pivotal role in compression molding, offering a unique combination of properties that make them ideal for this process. These materials are typically composed of a polymer matrix, such as thermosetting resins like polyester, epoxy, or vinyl ester, and reinforcing fibers such as glass, carbon, or aramid fibers. The reinforcement fibers provide the material with excellent tensile strength and stiffness, while the polymer matrix ensures that the load is evenly distributed throughout the part. This results in components that are not only strong but also lightweight, making them perfect for applications where weight reduction is crucial.
Applications Across Industries
Automotive Industry
The automotive sector is one of the largest consumers of compression-molded parts. Compression molding is used to produce a wide range of components, from large vehicle panels and bumpers to smaller, more intricate parts such as engine covers and interior trim. The ability to create parts with complex geometries and high dimensional accuracy makes compression molding an ideal choice for this industry. Moreover, the use of composite materials allows for significant weight reduction, which is essential for improving fuel efficiency and overall vehicle performance
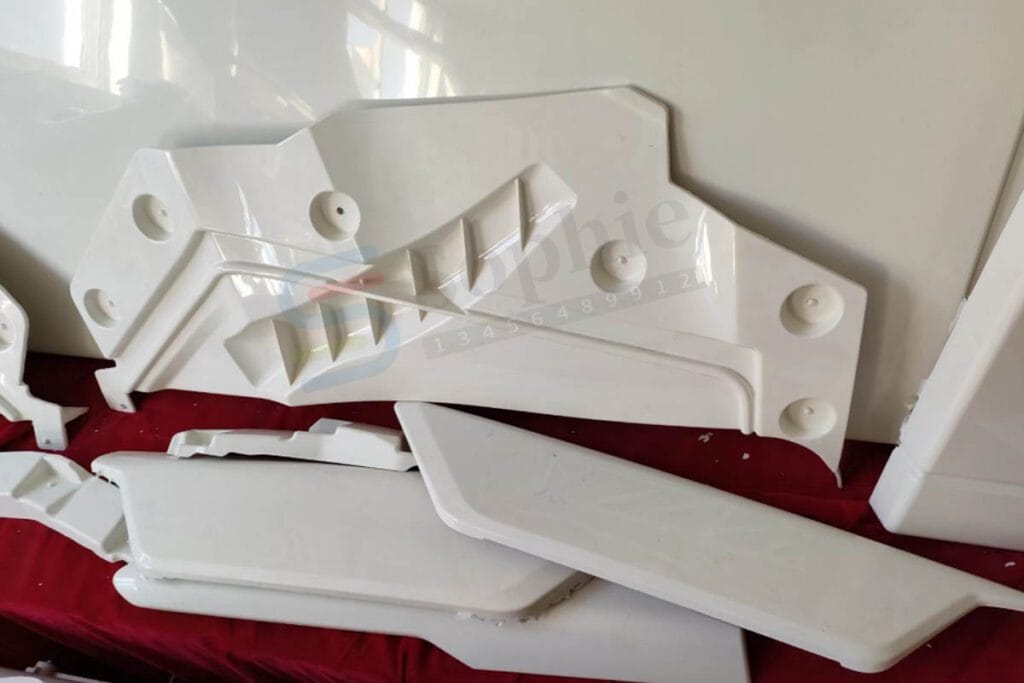
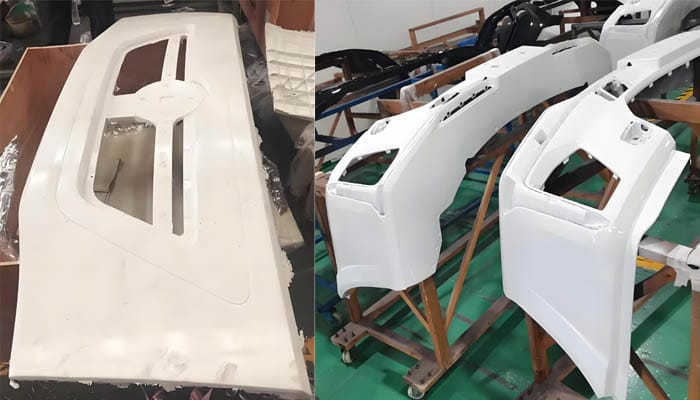


Aerospace Industry
In the aerospace industry, weight reduction is of paramount importance. Compression molding is used to produce structural components such as C-channels, H-beams, U-sections, L-stringers, and T-strings, which are used in aircraft construction. These components are not only lightweight but also possess the necessary strength and durability to withstand the harsh conditions of flight. Additionally, compression molding is used to produce O-rings and other sealing components that are critical for the proper functioning of aircraft systems.
Electrical Industry
The electrical industry also benefits greatly from compression molding. Components such as insulators, circuit breaker casings, and switch housings are commonly produced using this process. The high dimensional accuracy and smooth surface finish of compression-molded parts make them ideal for these applications, where precise fit and function are essential. Furthermore, the use of thermoset composites ensures that these components are thermally stable and can retain their structure and mechanical properties across a wide temperature range
Consumer Goods
Compression molding is not limited to heavy industries; it also plays a significant role in the production of consumer goods. Items such as kitchenware, appliance parts, and sports equipment are often produced using this process. The ability to create parts with intricate details and a smooth surface finish makes compression molding an attractive option for manufacturers looking to produce high-quality consumer products at a reasonable cost
Types of Composite Materials Used in Compression Molding
Sheet Molding Compound (SMC)
SMC is a popular choice for compression molding due to its excellent flow properties and ability to produce parts with a high-quality surface finish. It is a glass-reinforced polymeric material that is ideal for producing large, flat components such as automotive body panels and institutional seating. SMC offers superior strength-to-weight ratios and can be tailored to meet specific application requirements by adjusting the fiber-to-resin ratio.

Bulk Molding Compound (BMC)
BMC is another widely used material in compression molding. It is known for its excellent flow properties and ability to produce parts with high precision and performance. BMC is a putty-like injection molding compound that is perfect for precision applications such as electrical components and small automotive parts. It is also dielectric, flame-resistant, and corrosion-resistant, making it suitable for a wide range of applications
Carbon Fiber
Carbon fiber is a high-performance material that is gaining increasing popularity in compression molding. It offers several advantages, including high stiffness, high tensile strength, low weight, high chemical resistance, and high-temperature tolerance. These properties make carbon fiber an ideal choice for applications in the aerospace, civil engineering, military, medical, and automotive industries, where high strength and lightweight are key requirements.
Glass Mat Thermoplastics (GMT)
GMT is a type of composite material that is commonly used in compression molding to produce semi-structural and structural components. It consists of glass fibers pre-impregnated with a thermoplastic matrix, offering a good balance of strength, stiffness, and impact resistance. GMT is particularly suitable for applications where high-volume production is required, as it can be processed quickly and efficiently.
Advantages of Compression Molding
- Compression molding offers several advantages that make it a popular choice for many manufacturers. Some of the key benefits include:
High Strength-to-Weight Ratios: The use of composite materials allows for the production of parts that are not only strong but also lightweight, making them ideal for applications where weight reduction is crucial. - Precision and Dimensional Stability: The matched die tooling used in compression molding ensures that even intricately detailed parts have consistent dimensions and surface finishes. The curing process of thermoset composites reduces shrinkage and warping, resulting in great dimensional precision and tight tolerance control.
- Cost-effective for Large-scale Production: Compression molding is highly efficient and can produce large volumes of parts quickly and consistently. This makes it an ideal choice for manufacturers looking to produce high-quality parts at a reasonable cost.
Compression molding is a versatile manufacturing process that has found applications in various industries, from automotive and aerospace to electrical and consumer goods. Its ability to work with composite materials, such as SMC, BMC, carbon fiber, and GMT, allows for the production of parts with high strength-to-weight ratios, precision, and dimensional stability. As technology continues to advance, compression molding is likely to remain a crucial process in the manufacturing of high-quality components for years to come.


