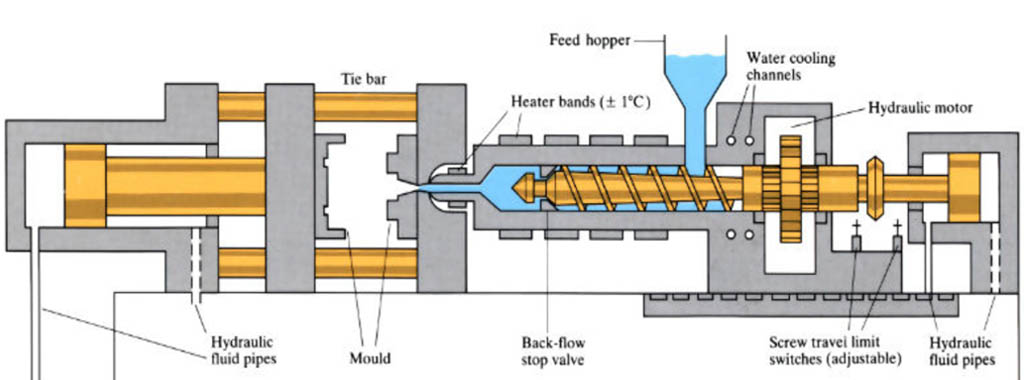
Injection molding is a manufacturing process used to produce parts or products by injecting molten material into a mold cavity. The process is commonly used in the production of plastic parts, but can also be used with metals, glass, ceramics, and other materials.
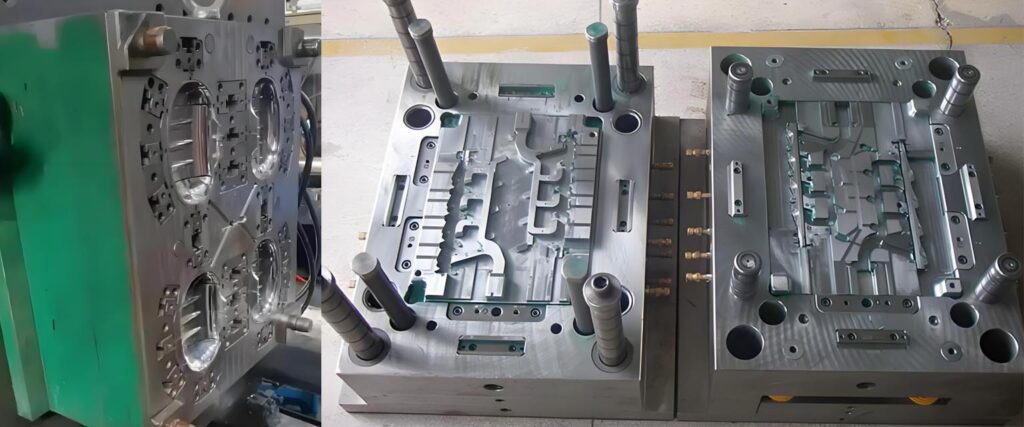
The injection molding process starts with the raw material being melted and then injected into a mold cavity, which is typically made of steel or aluminum. The molten material is then cooled and solidified, forming the final product.
The injection molding process has several advantages over other manufacturing processes. It allows for high production volumes, consistent part quality, and a wide range of part sizes and shapes. Additionally, the process can be automated, reducing labor costs and improving efficiency.
There are several important factors to consider when designing a part for injection molding, including material selection, wall thickness, and part geometry. The design of the mold is also critical, as it can impact part quality, production efficiency, and tooling costs.
Injection molding is widely used in industries such as automotive, consumer goods, medical devices, and electronics. With advancements in materials and technology, injection molding is likely to remain a popular manufacturing process for many years to come.