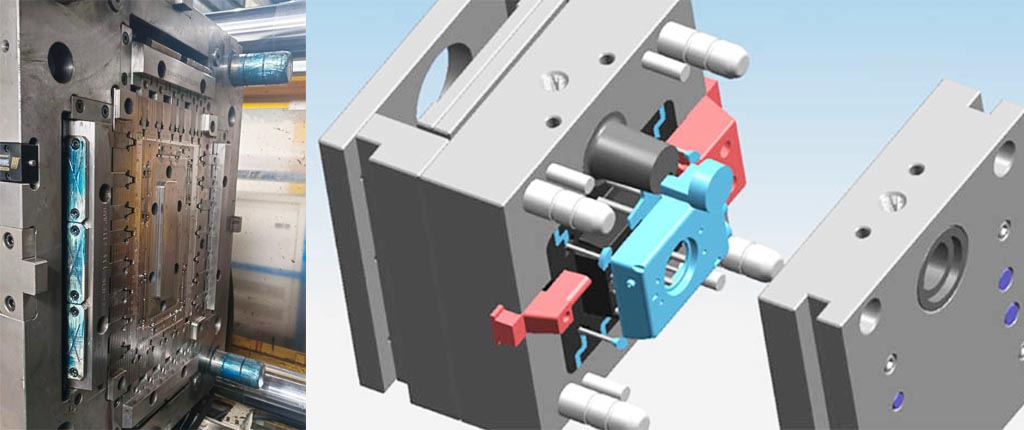
Key Precautions for Injection Mold Testing,injection mold testing is a crucial step in the manufacturing process to ensure product quality and consistency. However, to achieve accurate and reliable results, certain precautions must be taken. In this blog, we’ll explore the essential precautions that should be carefully considered during injection mold testing.
Table of Contents
ToggleKey Precautions for Injection Mold Testing
Before initiating the injection molding process for a new mold or when switching molds on the machine, conducting a mold trial is a crucial step. The outcomes of the mold test significantly impact the subsequent production efficiency of the factory. Consequently, during the mold testing process, it is imperative to adhere to proper operational procedures and meticulously record pertinent technical parameters. This practice ensures a seamless transition to mass production by facilitating informed decision-making based on the mold trial results.
1. Precautions prior to mold trial
Familiarize Yourself with Mold Details
Obtain the mold’s design drawings, conduct a thorough analysis, and involve mold technicians in the trial process for a comprehensive understanding.
Verify Mechanical Coordination on the Workbench
Prioritize a detailed examination for scratches, missing components, and any signs of looseness. Assess the mold’s sliding movements, check for potential leaks in water channels and air pipe joints, and, if applicable, mark limitations on the mold’s opening. Conducting these checks before mold installation helps prevent wasted hours by addressing issues upfront, avoiding the need to dismantle the mold after installation.
Verify Mechanical Coordination on the Workbench
Prioritize a detailed examination for scratches, missing components, and any signs of looseness. Assess the mold’s sliding movements, check for potential leaks in water channels and air pipe joints, and, if applicable, mark limitations on the mold’s opening. Conducting these checks before mold installation helps prevent wasted hours by addressing issues upfront, avoiding the need to dismantle the mold after installation.
Select a suitable trial injection molding machine
Once it is established that every component of the mold functions correctly, the next step is to select a suitable trial injection molding machine. When making this selection, it is crucial to consider:
(1) The injection volume capacity of the injection molding machine.
(2) The inner distance of the tie rod to ensure compatibility with the mold.
(3) Whether the moving itinerary of the movable template aligns with the requirements.
(4) The readiness of other essential test tools and accessories.
After confirming that everything is in order, the subsequent action is to hang the mold. During this process, it is essential to leave the hooks in place until all clamping templates are securely locked, and the mold is opened. This precaution prevents the possibility of clamping template loosening or breaking, ensuring the safety of the mold installation.
Once the mold is installed, conduct a meticulous check on the mechanical movements of each part. Examine components such as the sliding plate, ejector pin, retraction structure, and limit switch to ensure correct functionality. Pay special attention to the alignment of the injection nozzle and feeding port.
Shift focus to the mold closing action, lowering the mold closing pressure. During the manual and low-speed mold closing actions, carefully observe for any signs of unsmooth movements or abnormal sounds. While hoisting the mold is generally a straightforward process, the critical aspect is the meticulous adjustment of the mold gate and nozzle, often accomplished using test paper for precision.
Elevate Mold Temperature
Based on the product’s raw material characteristics and mold size, select an appropriate mold temperature controller to raise the mold temperature to the required production level. After increasing the mold temperature, it is imperative to recheck the movement of each component. The thermal expansion of the steel may lead to mold jamming, so closely monitor the sliding of each part to prevent strain and vibration.
Implementation of Experimental Plan Rules
If the factory does not adhere to an established experimental plan, it is advisable to adjust one condition at a time when modifying test conditions. This approach helps distinguish the impact of individual condition changes on the product, ensuring a systematic and controlled testing process.
Moderate Baking of Raw Materials
Depending on the raw materials used, moderately bake the original loaf to optimize its properties for the molding process.
Consistency in Raw Materials
For both mold trials and future mass production, use the same raw materials whenever possible to maintain consistency in product quality.
Avoid Inferior Materials
Exercise caution and refrain from testing the mold with inferior materials. If color specifications are essential, conduct a separate color test.
Addressing Internal Stress Issues
Internal stress problems can impact secondary processing. After the mold trial, stabilize the product by adding a secondary processing mold. Close the mold at a slow speed, adjust the clamping pressure, and perform multiple actions to check for uneven clamping pressure, minimizing the risk of burrs and mold deformation.
Once the preceding steps have been meticulously checked, proceed to reduce the mold closing speed and pressure. Set the buckle rod and ejector stroke, followed by adjustments to the standard mold closing speed. When adjusting the mold opening stroke, especially if the limit switch is involved, ensure it is slightly shorter. Terminate the high-speed mold opening action just before reaching the full mold opening stroke. This precaution is essential as the high-speed action stroke exceeds the length of the low-speed one throughout the entire mold opening process.
For plastic machines, additionally adjust the mechanical ejector rod to engage after the full-speed mold opening action. This ensures that the ejector plate or peeling plate is not deformed by excessive force, enhancing the overall durability of the components.
Prior to mold release, it is crucial to reevaluate the following aspects
Verify the adequacy of the feeding stroke, avoiding both excessive or insufficient strokes.
Check the pressure levels, ensuring they are within the optimal range and avoiding extremes of too high or too low pressures.
Assess the filling speed to strike a balance between being neither too fast nor too slow.
Examine the processing cycle duration to prevent potential issues such as short shots, breakage, deformation, burrs, or mold damage.
The risk of short shots, breakage, deformation, burrs, and potential mold damage can be mitigated through a careful evaluation of the processing cycle. If the cycle is too short, there’s a risk of the thimble pushing through the product or peeling the ring, potentially resulting in product crushing, which may necessitate hours to remove. Conversely, an excessively long processing cycle can lead to the breakage of thin core parts due to rubber compound shrinkage.
While it might be impossible to anticipate all potential issues during the mold tryout process, thoughtful consideration and prompt action can help avoid significant and costly losses.
By carefully considering these precautions during injection mold testing, manufacturers can enhance the reliability and efficiency of their production processes. Implementing a comprehensive approach to testing not only ensures high-quality end products but also contributes to the overall success of the manufacturing operation.