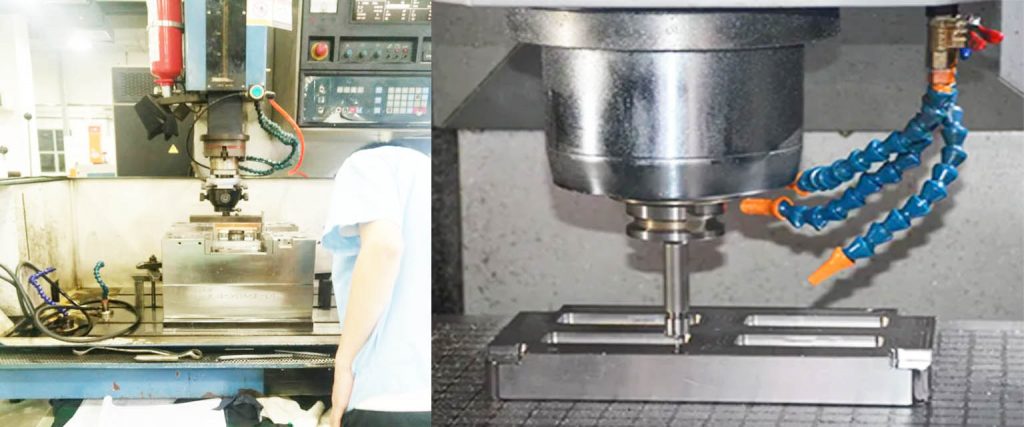
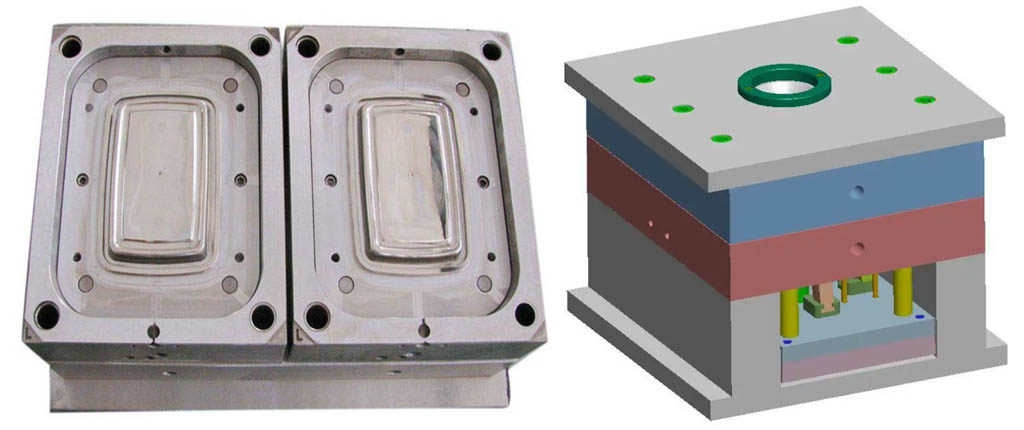
This article aims to help the car lamp mold industry to be invincible in the fiercely competitive market in the post-epidemic era by introducing the material selection of the steel for lamp mold.Car lights, known as the eyes of the car, are the core exterior parts with strong consumption driving force on the body, and are a must-change item for every size change of the car. The shape and design of car lights have a significant impact on car consumers. In the trend of car electronics, personalization and the rise of new energy vehicles, the cost of car lights in the whole vehicle is also increasing. The lamp mold is an indispensable and important production tool in the lamp industry.
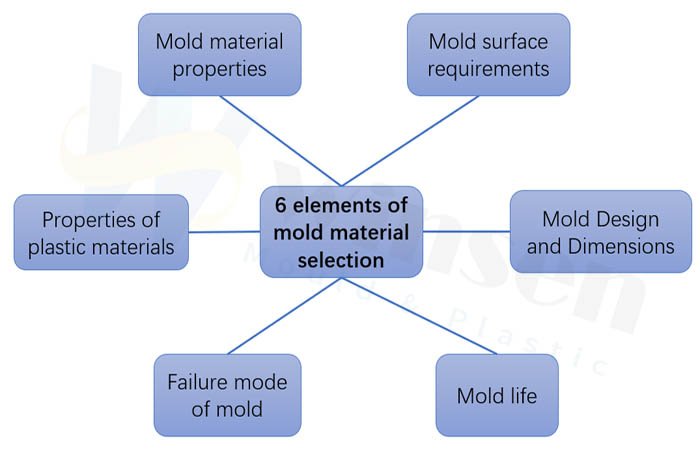
6 elements of mold material selection for lamp mold
There are many varieties and specifications of car lamp molds, complex shapes, and large drop. The requirements for the surface of the cavity are high, and the manufacturing is difficult. Therefore, a comprehensive analysis of various factors is required before material selection, as shown in the figure below: We think the factors that need to be considered include or aatters needing attention in the selection of lamp mold steel:
Table of Contents
ToggleCharacteristics of car lamp mold materials
Such as strength, toughness, wear resistance, corrosion resistance, weldability, hardenability, polishing, electrical discharge machining, surface treatment, etc.
Characteristics of molding materials
For example, whether the plastic is thermoplastic or thermosetting, whether a large amount of reinforcing agent is added to the plastic, whether the plastic is corrosive to the mold surface, etc.
Design and size of the car lamp mold
The more complex the structure of the mold and the larger the size, the higher the requirements for the toughness of the mold material.
Surface requirements of the car lamp mold
The surface roughness of the plastic mold is divided into 12 grades according to the American SPI standard, and is classified into four categories, A-mirror: usually polished with diamond paste, B-smooth: usually polished with sandpaper, C-semi-gloss Surface: usually polished with whetstone, D—Conventional surface: usually sandblasted, the lamp cavity usually requires SPIA1 or above polishing degree.
The service life of the car lamp mold
As the molding cycle of the mold and the quality requirements of the plastic parts are different, the normal wear level of the mold during use is also different. The American Society of Plastics Industry divides the mold of the injection molding machine of 400t or less into five levels: 101 type – mold Molding cycle number > 1 million mold times, used for products with extremely high output, hardness of mold cavity and other accessories ≥ HRC48; 102 type — mold molding cycle number is between 500,000 and 1 million mold times, used for high For high-volume products, the surface hardness of the cavity is ≥HRC48, and other functional parts should be heat treated; Type 103—the number of mold forming cycles is between 100,000 and 500,000 mold times, for medium-volume products, the surface hardness of the cavity is ≥ HB300; 104 type — the number of mold forming cycles can reach up to 100,000 mold times, for low-volume products, the fixed mold can be annealed mold steel or aluminum alloy; 105 type — mold molding cycle times < 500 mold times , for the production of a limited number of products, the mold material requirements are low, and the price should be as cheap as possible, cast steel materials or epoxy resins can be selected.
Failure mode of car lamp mold
As mentioned above, the main failure modes of lamp molds include cracking, surface defects such as poor polishing effect, early failure of molds and mold material characteristics, molding material characteristics, mold design, mold surface requirements and service life and other factors ring Interlocked and closely related. Understanding the failure modes of the mold under different working conditions and finding out effective preventive measures is conducive to the correct selection of mold materials.
The important criterion for mold material selection should not be the initial cost of the material, but the life cycle cost or cost-effectiveness. Under normal circumstances, the cost-effectiveness will be improved by selecting the most cost-effective mold materials that are most suitable for mold requirements. This is the way to survive and progress in China’s mold industry in today’s highly competitive industry background.