What is gate in injection moulding ? The gate, also known as the feed gate, refers to a passage from the runner to the mold cavity, which is the smallest and shortest part of the gating system. In metal casting, it refers to the entrance and passage of molten metal into the mold when pouring. Often refers to the gating system. The function is to use the compressed flow surface to accelerate the feed, and the high shear rate can make the feed flow better; After the molding is completed, the gate is first cured and sealed, which has the function of preventing the backflow of the feed and preventing the pressure of the cavity from dropping too fast to cause shrinkage and depression of the molded product. After injection moulding, it is easy to cut off to separate the runner system and the profile.
Table of Contents
Toggle1. Overview of gates in injection moulding
The gate can be understood as the last “door” for molten plastic to enter the cavity through the gating system, which is the feed channel connecting the runner and the cavity. It has two functions: first, it controls the flow of plastic melt into the cavity; second, when the injection pressure is removed, the cavity is blocked, so plastic will not flow back if it is not cooled and solidified in the cavity.
What is gates in injection moulding
The choice of gate type depends on factors such as product appearance requirements, size and shape constraints, and the type of plastic used. The shape and size of the gate have a great influence on the quality of the plastic parts. In most cases, the gate is the part with the smallest cross-sectional size in the runner (except for the main gate type), and the ratio of its cross-sectional area to the cross-sectional area of the runner is about 0.03-0.09, the cross-sectional shape is mostly rectangular or circular, and the gate step length is about 1-1.5mm.
2. What are the advantages of using small gates in general
(1). The small gate can increase the flow rate of the material passing through. There is a large pressure difference between the two ends of the small gate, which can reduce the apparent viscosity of the molten plastic and make it easier to fill the mold.
(2). The small gate can increase the temperature of the molten plastic and increase the fluidity. The frictional resistance at the small gate is large. When the molten plastic passes through the gate, a part of the energy is converted into frictional heat to heat up, which is very beneficial to improve the quality of thin-walled plastic parts or plastic parts with fine patterns.
(3). Small gate can control and shorten the feeding time, reduce the internal stress of plastic parts, and shorten the molding cycle. During injection, the pressure holding stage continues until the gate is condensed. The small gate condenses quickly and the feeding time is short, which reduces the coagulation orientation and coagulation strain of macromolecules, and greatly reduces the internal stress of the feeding. The adaptation and sealing of the small gate can also control the feeding time correctly and improve the quality of the plastic parts.
(4). Small gate can balance the feeding speed of each cavity. The outlet resistance of the small gate is much larger. Only after the runner is full and has sufficient pressure, each cavity can be filled at a similar time, which can improve the imbalance of the feeding speed of each cavity.
(5). It is convenient to trim plastic parts. Small gates is easy and quickly removed by hand. After the small gate is removed, the traces are small, which reduces the grinding time. However, a gate that is too small will greatly increase the flow resistance and prolong the filling time. For molten plastics with high viscosity and shear rate that have little effect on the apparent viscosity, small gates should not be used.
The gate is also called the feeding port. It is a narrow opening between the runner and the cavity, and it is also the shortest part. Its function causes the molten plastic to accelerate when it enters the cavity, which is conducive to quickly filling the cavity and pouring after molding. The plastic is condensed first to seal the cavity, prevent the molten plastic from flowing backwards, and prevent the cavity pressure from dropping too fast, so that shrinkage holes or depressions occur on the product, and it is easy to separate the pouring aggregate from the product after molding.
3. Gate form and application
(1) Direct gate, the melt enters the cavity directly from the nozzle through the gate, the process is short, the feeding speed is fast, and the molding effect is good. Because the cross section of the sprue is generally larger, the pressure and heat losses are small, and the pressure-holding and feeding effect is strong. Moreover, the mold has a simple structure, is easy to manufacture, and has a low cost. Its disadvantages are: the cross-sectional area of the straight gate is large, it is difficult to remove the gate, and the trace after the gate is removed is more obvious, which affects the appearance of the product.
(2) Side gate, also known as rectangular gate. It is generally set on the parting surface and is fed from the outside of the cavity. Since the size of the side gate is generally small, the relationship between the cross-sectional shape and the pressure and heat loss can be ignored. The shape of the side gate is simple, the processing is convenient, the size is easy and accurate to control, and it is easy to change quickly. It is suitable for all plastic materials,but it is not suitable for polycarbonate (PC). The disadvantage is that there are obvious gate defects on the surface of the product, and the gate needs to be manually cut off. It is easy to produce flow marks during molding, which is not suitable for thin plate-shaped transparent products, and also not suitable for thin and long barrel-shaped products.
(3) Point gate, also known as needle gate. The point gate can be applied to various forms of products. The residual stress near the gate is small, the gate can be broken by itself, and automatic production can be realized. For larger products, multiple points can be fed at the same time, which can shorten the process and reduce the The deformation phenomenon caused by flow resistance occurs, but the injection pressure loss is large, and the injection molding pressure is larger than that of the direct gate. Most of them use a three-plate mold (also known as double-parting surface) structure, the mold structure is more complex, and the molding cycle longer.
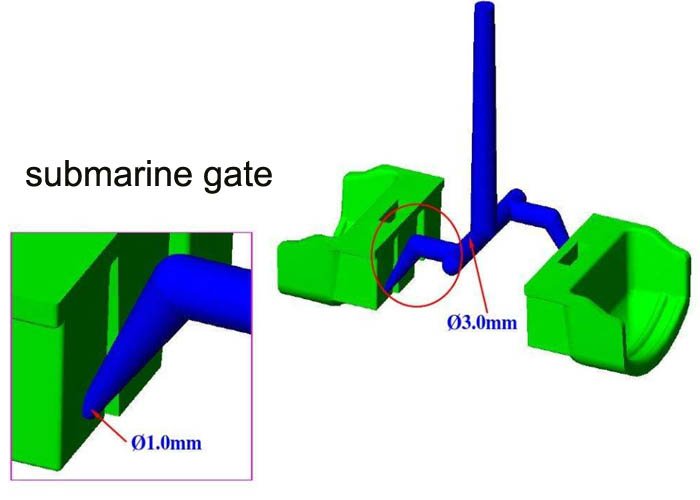
(4) Latent gate, also known as tunnel gate.
The submerged gate can be machined to the exact size, and there is no fit problem in the shape. When the gate is demolded, it can be automatically cut off from the product, which is suitable for automated production. However, it is recommended that PC, PMMA and SAN products should not be used.
(5) Ear gate, also known as ear protection gate, wing gate. It is suitable for all plastic products that do not allow gate marks on the appearance surface, which can reduce flow marks caused by side gates. The gate is attached to the surface of the finished product, and special care must be taken to remove the gate defect. PVC, PU plastic products should not use this method.


