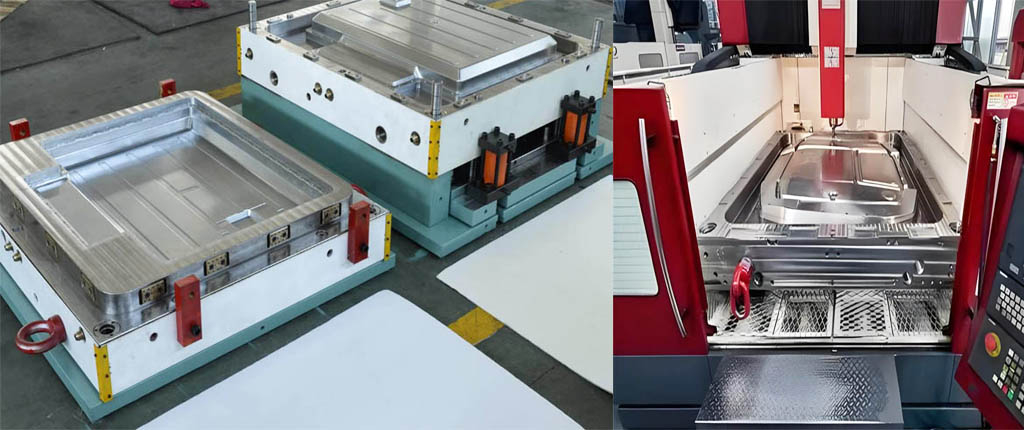
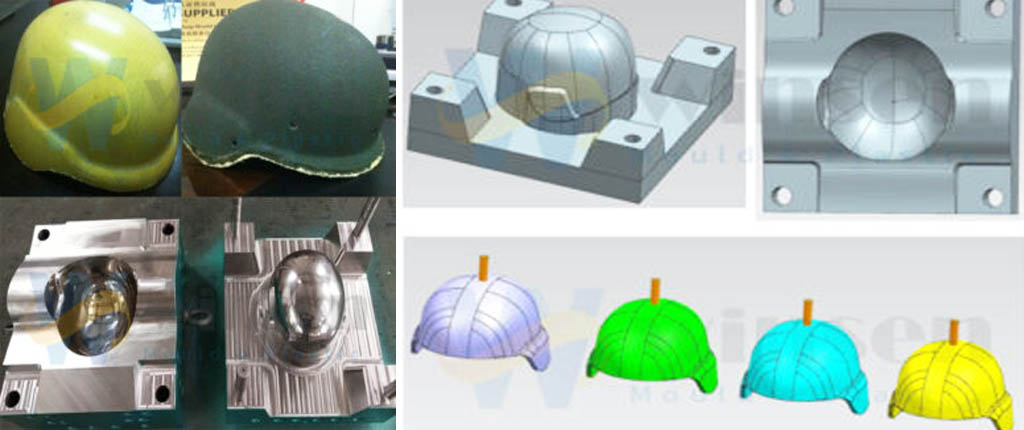
What Is SMC sheet molding compound Mold? Sheet Molding Compound (SMC) molds are essential tools in the production of high-quality composite parts used across various industries. SMC mold is compression molding process.
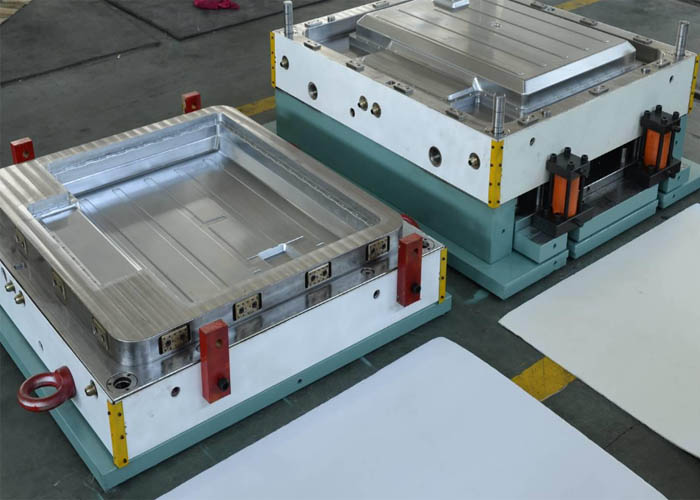
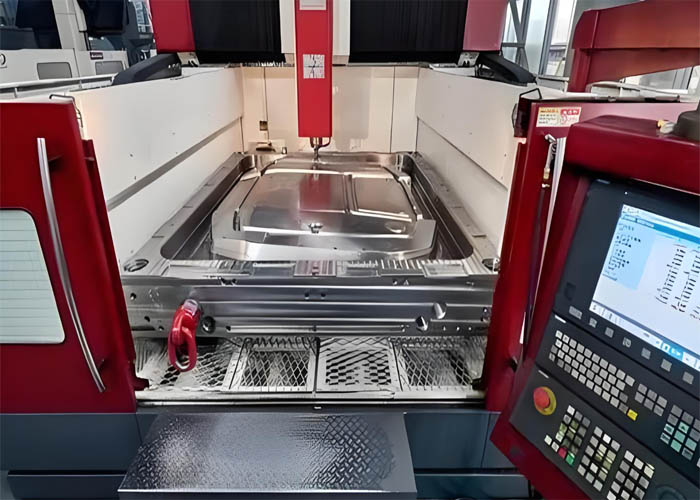


Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is SMC(sheet molding compound)
SMC or Sheet Molding Compound, is a composite material comprising a blend of polymer resin, inert fillers like calcium carbonate, talc, or wollastonite, fiber reinforcement, catalysts, pigments, stabilizers, release agents, and thickeners. The glass reinforcement content typically ranges from 10% to 60%, with fiber lengths slightly longer than those found in Bulk Molding Compounds (BMC).
SMC’s production process ensures thorough integration of fibers and resins. This manufacturing method operates as a continuous in-line process. Typically, SMC is composed of either fiber impregnated with resin paste or a chopped fiber mat enveloped between polyhexene film layers on both sides to prevent sticking and ensure handling ease during transportation and storage.
What Is SMC Mold
An SMC mold is crafted from high-strength steel plates with meticulously polished surfaces, ensuring the impeccable surface quality of the molded SMC parts. Distinguished by its compression process, this mold compresses the SMC material to form the final product. Typically, SMC compression molding employs a hydraulic press machine, with the cavity and core affixed to the top and bottom platens. As the material is introduced into the open mold, the platens close, initiating the heating process. Subsequently, the press pressure compels the SMC material to uniformly flow throughout the mold cavity, resulting in the desired shape.
Tensile strength characteristics of SMC molds
SMC fiberglass molds have attracted much attention for their specific performance and wide range of applications. Among them, tensile strength, as one of the important indicators to measure its performance, is of great significance for ensuring the durability and stability of the product.
Tensile strength refers to the maximum force that a material resists breaking under tension. For FRP molds, the level of tensile strength directly affects its deformation and fracture risk during the force process. Generally speaking, high-quality products have higher tensile strength and can withstand greater tensile forces in complex working environments to ensure the stable operation of the product.
In practical applications, the tensile strength of FRP molds is affected by many factors. For example, the material, manufacturing process, use environment, and maintenance methods of the product will affect its tensile strength. Therefore, when selecting and using the product, these factors need to be considered comprehensively to ensure that it has good tensile strength and meets specific work requirements.
At the same time, improving the tensile strength of FRP molds is also an important goal in the manufacturing process. By optimizing the material formula, improving the manufacturing process, and strengthening quality control, the tensile strength of the product can be effectively improved, making it more durable and reliable during use.
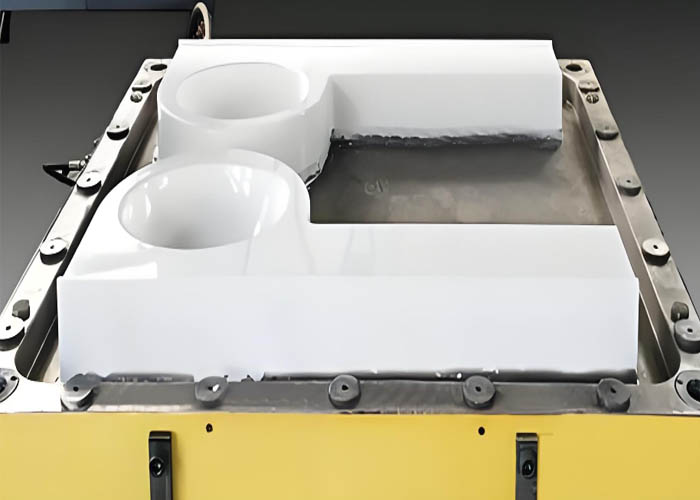

Key points of SMC mold design
Compounds’ color can be tailored according to preferences.
Options like in-mold coatings and vacuum systems enhance surface paintability, obviating the necessity for priming.
Mold design considerations encompass parting lines, shear edge configurations, ribs and inserts, surface roughness, and draft angles.
SMC compression machines typically operate within a temperature range of 140 to 160 degrees Celsius.
High-quality steel is commonly employed in crafting male and female molds, except when the temperature remains below 400 psi.
SMC molds necessitate heated channels, commonly facilitated through steam, oil, electricity, or high-pressure water heating systems.
SMC compression molding processing
SMC compression molding stands as an advanced method for shaping composite materials. It enables the continuous production of high-strength, intricate parts across a diverse range of sizes. Operating within a “compression molding press,” typically powered hydraulically, SMC molding involves the placement of material charge into the mold, followed by the closure of heated mold halves and the application of pressure, often reaching up to 2,000 psi. The cycle time varies between one to five minutes, contingent upon the part’s size and thickness. Notably, features like ribs, bosses, and inserts can be intricately formed through compression molding, allowing for the creation of complex SMC parts with exceptional accuracy.
Initiating the SMC product pressing process entails securing SMC tooling onto the press’s platen, heating the SMC tooling, and introducing the SMC material into the open mold. Subsequently, parameters for the SMC tooling molding process, such as pressure, curing time, opening and closing speed, are configured. The tooling is then closed, and upon demolding, the molded SMC product is extracted from the tooling.
Modulus characteristics of SMC fiberglass and its influencing factors
SMC FRP is a composite material made of glass fiber reinforced plastic, and its performance is superior to traditional materials in many aspects. Among these performance parameters, modulus is an important indicator of material rigidity. Usually we discuss the elastic modulus of the material, also known as Young’s modulus, which represents the material’s ability to resist deformation.
The modulus of SMC FRP is affected by many factors, including the type of fiber, arrangement direction, volume fraction, and the properties of the matrix resin. Generally speaking, it has a higher elastic modulus and can provide good structural support and bending resistance. For example, when the fibers are arranged in a specific direction, the modulus of the material in that direction will be higher.
In addition, the modulus is also related to temperature. At low temperatures, the modulus of most FRPs will increase; at high temperatures, the modulus may decrease. Therefore, the temperature variation range of the application environment needs to be considered during design.
In practical applications, by optimizing these factors, the modulus of SMC FRP can meet specific design requirements. For example, in some structural parts that require high rigidity, the modulus can be increased by increasing the fiber content or changing the fiber arrangement. At the same time, by selecting a suitable resin system, the thermal stability and durability of the material can be improved.
SMC mold professional manufacturer
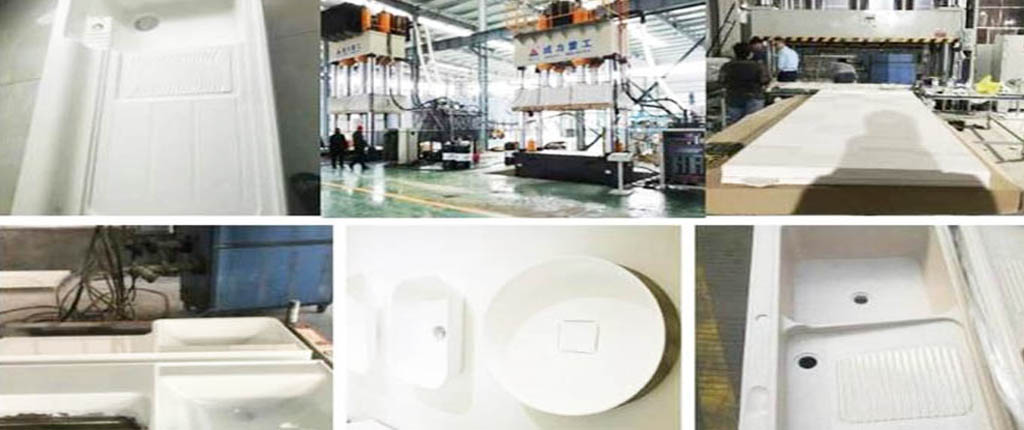
As a leading SMC mold manufacturer in China, WS has extensive experience in this field, having successfully developed various projects including SMC helmet molds, SMC mamhole cover molds, SMC meter box molds, SMC bumper molds, bathtub molds, SMC shower tray molds, and SMC wash basin molds. We offer comprehensive services in mold design, fabrication, and testing to meet your specific requirements. Leverage our expertise to ensure high-quality, precise molding solutions tailored to your needs.
The advantages of SMC finished products
Compression molded SMC parts are distinguished by their diverse sizes and shapes, excellent surface finishes, and exceptional consistency from part to part.
Molded-in color options are available through pigmentation.
Minimal trimming and finishing costs.
Excellent dimensional stability, thermal resistance, and chemical resistance.
Precision SMC molds with mirror finishes can achieve automotive-grade A-grade surfaces.
A variety of SMC material ratios allows customization to better meet environmental requirements.
Achieve approximately 50% weight reduction compared to metal and around 30% reduction compared to other thermoplastics.
In summary, SMC (Sheet Molding Compound) molds play a crucial role in the production of high-quality composite parts. These molds, crafted from robust steel and designed for precision, enable the manufacturing of complex, durable components with excellent surface finishes. The SMC compression molding process ensures high repeatability, making it ideal for producing large volumes of parts with consistent quality.
From customizable colors to minimal finishing costs, and from superior dimensional stability to significant weight reductions compared to metals and other thermoplastics, SMC molds offer numerous advantages. As the demand for lightweight, high-strength components continues to grow across various industries, the importance and utility of SMC molds are set to increase even further.
Whether you are in the automotive, aerospace, or consumer goods industry, understanding the capabilities and benefits of SMC molds can help you make informed decisions and optimize your manufacturing processes.