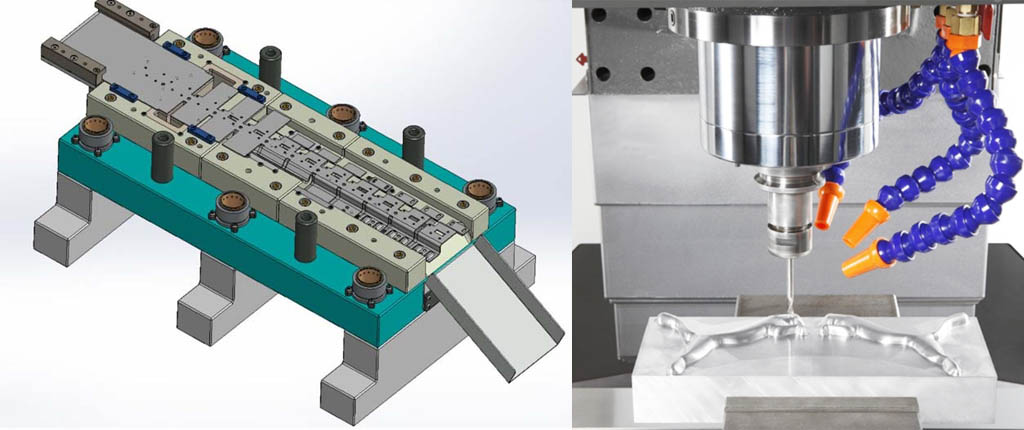
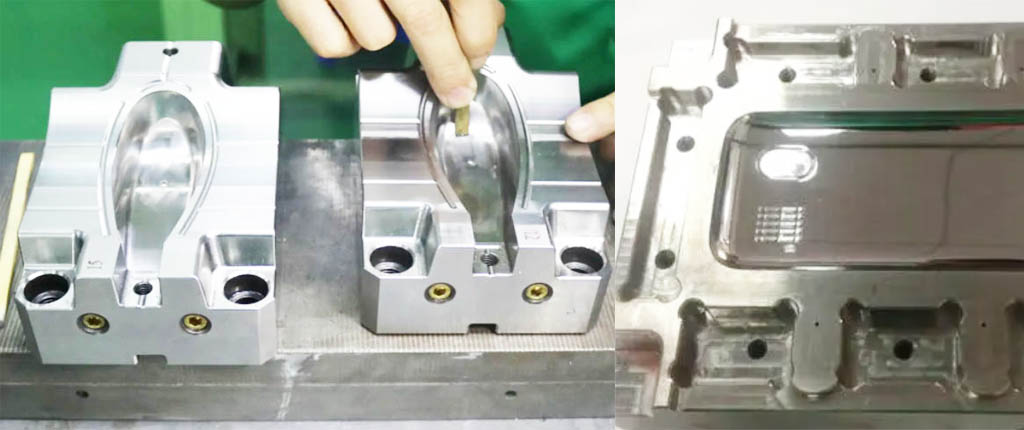
What is the mould process performance? In general,mold process has to go through several processes such as forging, cutting, and heat treatment ect.. The manufacturing quality of mould and reduce the production cost, the mold material should have good forgeability, machinability, hardenability and grindability; it should also have small oxidation, decarburization sensitivity and quenching properties. Deformation and cracking tendency.
Table of Contents
Toggle1. Forgeability-mould process performance
Low hot forging deformation resistance, good plasticity, wide forging temperature range, low tendency for forging cracking and cold cracking and precipitation of network carbides.
2. Annealing manufacturability
The spheroidizing annealing temperature range is wide, the annealing hardness is low and the fluctuation range is small, and the spheroidization rate is high.
3. Machinability
Large cutting amount, low tool loss and low surface roughness.
4. Sensitivity to oxidation and decarburization
When heated at high temperature, it has good anti-oxidation performance, slow decarburization rate, insensitivity to heating medium, and small tendency to produce pitting.
5. Hardenability
It has uniform and high surface hardness after quenching.
6. Hardenability
After quenching, a deep hardened layer can be obtained, which can be hardened by using a mild quenching medium.
7. Quenching deformation and cracking tendency
Conventional quenching volume changes are small, the shape is warped, the distortion is slight, and the abnormal deformation tendency is low. Conventional quenching has low cracking sensitivity and is not sensitive to quenching temperature and workpiece shape.
8. Grindability
The relative loss of the grinding wheel is small, the limit grinding amount without burn is large, it is not sensitive to the quality of the grinding wheel and cooling conditions, and it is not easy to cause abrasion and grinding cracks.
The performance of a mold process can be evaluated based on several key factors. These include:
(1).Quality of the molded product: The quality of the product is an important factor in evaluating the performance of a mold process. The mold should be able to consistently produce parts that meet the required specifications, including dimensional accuracy, surface finish, and material properties.
(2).Cycle time: The cycle time is the time it takes to produce one complete part, including the time for molding, cooling, and ejection. A shorter cycle time means more parts can be produced in a given time period, which can improve the overall efficiency of the process.
(3).Scrap rate: The scrap rate is the percentage of molded parts that do not meet the required specifications and are therefore unusable. A lower scrap rate means that the process is more efficient and produces less waste.
(4).Equipment uptime: The amount of time the mold process is operational and producing parts is important in evaluating its performance. Equipment downtime can result in lost production time, increased costs, and reduced efficiency.
(5).Maintenance requirements: The mold process requires regular maintenance to ensure that it continues to operate at peak performance. A well-maintained mold process will have fewer breakdowns, lower maintenance costs, and higher efficiency.
Overall, a well-designed mold process with good performance can result in high-quality parts, lower production costs, and increased profitability.