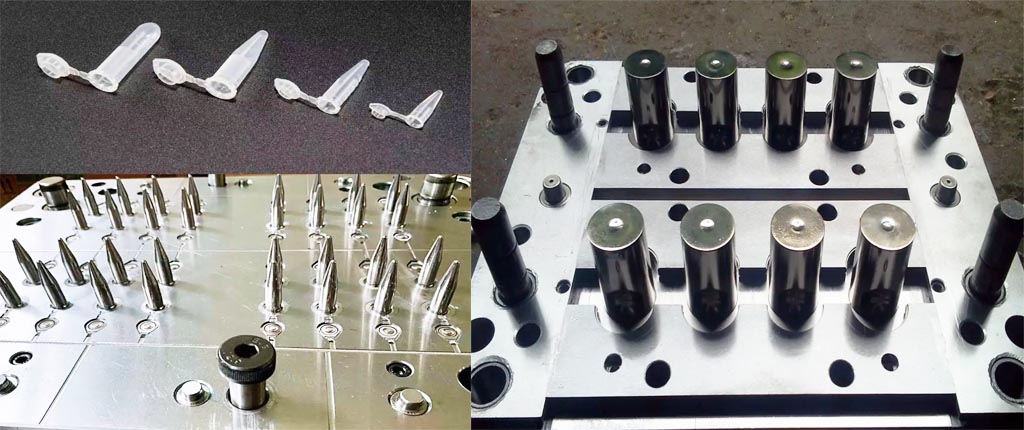
What is virus sampling storage tube? Understanding Virus Sampling Storage Tubes: A Vital Tool in Disease Research and Diagnostics.In the realm of virology and disease research, precision and accuracy are paramount. Virus sampling storage tubes, a critical component in the collection, preservation, and transport of viral specimens, have become indispensable tools for researchers and healthcare professionals worldwide. In this blog, we’ll delve into the world of virus sampling storage tubes, exploring their importance, types, and best practices for their use.
Table of Contents
Toggle
What is virus sampling storage tube
Virus preservation tube is also called virus sampling preservation tube. It is suitable for sampling and preservation of influenza virus (common influenza, highly pathogenic avian influenza, influenza A H1N1 virus, etc.), hand, foot and mouth virus and other types of viruses. It is also used for sampling and preservation of mycoplasma, chlamydia, ureaplasma, etc.
The Significance of Virus Sampling Storage Tubes
1. Disease Diagnosis
Virus sampling storage tubes are essential for preserving clinical samples such as swabs, blood, or bodily fluids for accurate disease diagnosis. They help ensure that viral specimens remain stable and viable during transportation to the laboratory.
2. Research
Researchers rely on virus sampling storage tubes to store and transport viruses for in-depth studies, including genetic analysis, vaccine development, and antiviral drug testing. These tubes safeguard the genetic material of the virus, allowing scientists to work with accurate and representative samples.
3. Epidemiology and Surveillance
In the context of disease outbreaks or pandemics, the timely collection and safe transport of viral samples are crucial for epidemiological studies. Virus sampling storage tubes facilitate this process, aiding public health efforts to track, understand, and mitigate the spread of infectious diseases.
Types of Virus Sampling Storage Tubes
Several types of virus sampling storage tubes are available, each tailored to specific applications
1. Viral Transport Media (VTM) Tubes
These tubes contain a specialized transport medium designed to maintain the viability of the virus while preventing bacterial contamination. VTMs are commonly used for clinical specimen collection.
2. Cryovials
Cryovials are designed for long-term storage of viral specimens at ultra-low temperatures, typically in the range of -80°C to -196°C. These tubes are ideal for archiving samples for extended research projects.
3. Inactivation Tubes
Inactivation tubes contain chemical agents that inactivate viruses, making the specimens safe for handling outside of high-containment labs. They are often used when studying highly pathogenic viruses.
4. Saliva Collection Tubes
With the rise of non-invasive sampling methods, saliva collection tubes have gained popularity. They allow for easy, painless collection of viral specimens.
Best Practices for Using Virus Sampling Storage Tubes
To ensure the reliability of viral specimens, it’s crucial to follow best practices when using virus sampling storage tubes
1. Proper Labeling
Clearly label each tube with essential information, including the patient’s identification, date of collection, and sample type.
2. Aseptic Techniques
When collecting specimens, maintain strict aseptic techniques to prevent contamination.
3. Cold Chain Maintenance
Maintain the cold chain for samples that require refrigeration or freezing to preserve the virus’s integrity.
Special instructions for the use of virus storage tubes
1. Unused virus storage tubes can be stored at room temperature and away from light;
2. Freshly collected clinical specimens should be transported to the laboratory within 48 hours at 2-8°C; those that cannot be delivered to the laboratory within 48 hours should be stored at -70°C or below.
3. Specimens should be inoculated and separated as soon as possible after they are sent to the laboratory. Those that can be inoculated and separated within 48 hours can be stored at 2-8°C. If it cannot be inoculated, it should be stored at -70°C or below.
Virus sampling storage tubes are unsung heroes in the world of virology and disease research. Their careful selection, proper use, and adherence to best practices are vital to maintaining the integrity of viral specimens, whether for diagnostic purposes, research endeavors, or public health initiatives. As the field of virology continues to evolve, these tubes will remain indispensable tools in our quest to understand, combat, and control infectious diseases.